Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Initialising ...
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
Lecture Notes in Computer Science 10776, p.257 - 273, 2018/00
Times Cited Count:2 Percentile:50.01(Computer Science, Artificial Intelligence)A preconditioned Chebyshev basis communication-avoiding conjugate gradient method (P-CBCG) is applied to the pressure Poisson equation in a multiphase thermal-hydraulic CFD code JUPITER, and its computational performance and convergence properties are compared against a preconditioned conjugate gradient (P-CG) method and a preconditioned communication-avoiding conjugate gradient (P-CACG) method on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8,208 KNLs. The P-CBCG method reduces the number of collective communications with keeping the robustness of convergence properties. Compared with the P-CACG method, an order of magnitude larger communication-avoiding steps are enabled by the improved robustness. It is shown that the P-CBCG method is 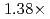 and
and 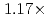 faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
faster than the P-CG and P-CACG methods at 2,000 processors, respectively.
Ogawa, Masuro; Shiina, Yasuaki; Fumizawa, Motoo; Takeda, Tetsuaki; Takada, Shoji; Kubo, Shinji; Inaba, Yoshitomo
JAERI-Tech 98-062, 126 Pages, 1999/01
no abstracts in English
*; *
Nihon Keisan Kogakkai Rombunshu, 1, p.27 - 33, 1999/00
no abstracts in English
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
This talk reviews exascale computing technologies in fusion plasma simulations developed under the Post-K priority issue. Burning plasmas in ITER consists of multi-species ions, and their spatio-temporal scales are more than an order of magnitude larger than existing devices. Therefore, burning plasma simulations in ITER require exascale computing. To this end, we have developed novel computing technologies, which enables highly efficient computation on latest many core processors and reduces the inter-node communication, in the five dimensional fusion plasma turbulence code GT5D, and their performances were demonstrated on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8,208 XeonPhi7250 (KNL) processors.
Idomura, Yasuhiro
no journal, ,
This talk reviews computing technologies developed for extreme scale nuclear CFD simulations on latest many core computing platforms. At JAEA, there are needs for extreme scale CFD simulations for analyzing critical issues such as melt relocation behavior of nuclear reactors at severe accidents and environmental dynamics of radioactive substances. Although the latest many core platforms offer promising solutions for such high computing needs, accelerated computation reveals severe bottlenecks of inter-node communication and data I/O. To resolve these issues, we have developed novel communication-avoiding matrix solvers and an In-Situ visualization system for the three dimensional multi-phase and multi-component thermal hydraulic core, JUPITER, and their performances were demonstrated in on the Oakforest-PACS, which consists of 8,208 XeonPhi7250 (KNL) processors.
Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Mayumi, Akie; Yamada, Susumu; Matsumoto, Kazuya*; Asahi, Yuichi*; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
We propose a modified communication-avoiding generalized minimal residual (CA-GMRES) method, which reduces both computation and memory access by 30% with keeping the same CA property as the original CA-GMRES method. These numerical properties, less communication and computation with higher arithmetic intensity, are promising features for future exascale machines with limited memory and network bandwidths. The modified CA-GMRES method is applied to a large scale non-symmetric matrix in an implicit solver of the gyrokinetic toroidal five dimensional Eulerian code GT5D, and its performance is estimated on the Oakforest-PACS (KNL). The numerical experiment shows that compared with the generalized conjugate residual method, computing kernels are accelerated by 1.5x, and the cost of data reduction communication is reduced from 12.5% to 1% of the total cost at 1,280 nodes.
Mayumi, Akie; Idomura, Yasuhiro; Ina, Takuya*; Yamada, Susumu; Imamura, Toshiyuki*
no journal, ,
To improve the convergence property of the communication avoiding conjugate gradient (CA-CG) method is needed for applying it to ill conditioned problems such as the pressure Poisson equation in the multiphase CFD code JUPITER. In the CA-CG method, one can avoid more communication by increasing the number of CA steps. However, this makes the CA-CG method less robust against numerical errors. To resolve this problem, we apply the Chebyshev basis CG (CBCG) method to JUPITER.
Sato, Takumi; Hirata, Naoya*; Oikawa, Katsunari*; Nagae, Yuji; Kurata, Masaki
no journal, ,
Macroscopic segregation of molten core and melted components occurs with slow cooling rate in the accident of Fukushima Daiichi Nuclear Power Plants. The solidification model considering macroscopic segregation of molten core and melted components was developed in order to predict distribution of core elements. In this study, solidification and microscopic segregation were simulated with the Scheil model using thermal properties calculated by Thermo-calc. We estimated segregation behavior of molten core and investigated an influence of cooling conditions on macroscopic segregation.